The business environment is constantly changing. Organizations are adding new sites and staff or modifying applications to meet growing business needs.
So what is SD-WAN? SD-WAN makes it easier to connect locations while delivering sub-second network failover and application performance improvements. This solution also provides visibility into network usage so NetOps can manage traffic to maximize bandwidth utilization.
What is SD-WAN?
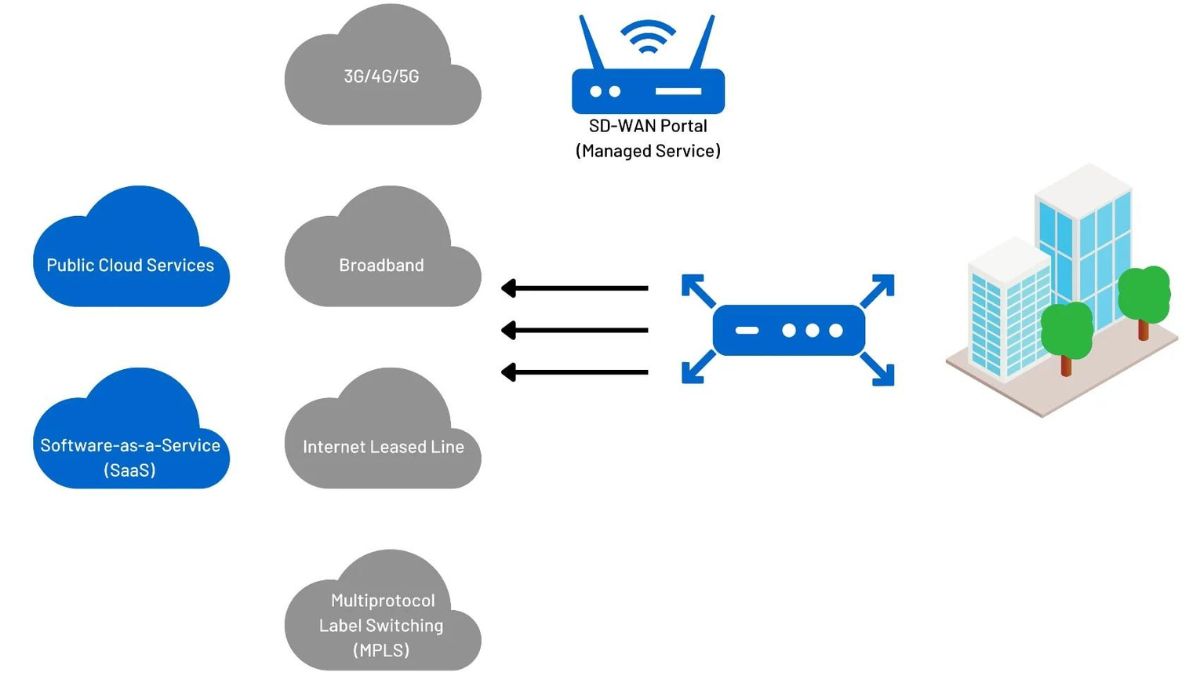
SD-WAN applies software-defined networking (SDN) principles to wide-area networks (WANs). The result is a dynamic, reliable, and cost-efficient network that enables applications to run across multiple connections, including the public Internet. This provides a competitive alternative to costly MPLS and private-line WAN services.
An SD-WAN combines the benefits of an Internet VPN with application performance and routing technology to provide better and more secure data communications over long distances between branch offices and cloud platforms. Typically, an SD-WAN solution consists of hardware or virtual devices deployed at each branch location and software running on CPE (customer premises equipment) at each site. The software monitors WAN connectivity, detects congestion and performance issues, and automatically selects the most suitable path for each application. For example, it may send voice-over-IP traffic over an MPLS connection if the other alternatives are not available or performing well. Otherwise, it may opt for a lower-cost broadband Internet or 4G LTE wireless circuit.
A business-driven SD-WAN also supports centralized orchestration, making it easy for IT to deploy new applications or make quality of service or security policy changes. This feature helps reduce network deployment time and minimizes human errors that could compromise performance or security. In addition, an SD-WAN can help a company lower its networking expenses by utilizing relatively inexpensive Internet connections for some types of traffic and reserving more expensive dedicated lines for mission-critical applications.
What are the Benefits of SD-WAN?
Several benefits can be realized by companies implementing SD-WAN. These include:
Increased network performance: SD-WAN enables businesses to deploy and scale their applications in the cloud, reducing costs by eliminating backhaul expenses. It also improves WAN efficiency by optimizing bandwidth for real-time application transmission by using multiple connection technologies, such as LTE, MPLS, and broadband Internet.
Reduced networking costs: Many organizations find that leveraging low-cost local broadband Internet and eliminating reliance on expensive MPLS connections can substantially save operating expenditures. By directing traffic over the best available connection, based on factors including performance and cost, SD-WAN can further reduce costs.
Enhanced security: By encrypting traffic traversing the WAN and employing other security measures, SD-WAN can help protect a company’s networks from dangers like malware, ransomware, and data breaches.
Simplified network management: Operating a WAN infrastructure has traditionally been complex and time-consuming. SD-WAN streamlines this effort by enabling a central controller to send operational policies to all deployed devices, governing traffic routing and other functions.
Moreover, the deployment models for SD-WAN can be customized to meet the needs of each business. For example, a large, geographically distributed company may want to establish regional points-of-presence (PoPs) that act as gateways for remote employees, giving them access to the enterprise’s networks without needing a VPN.
What are the Challenges of SD-WAN?
SD-WAN technology is a great way to enable businesses to easily connect their branches and data centers with cloud/SaaS applications. However, several challenges are associated with deploying and managing this type of infrastructure.
One of the biggest challenges is ensuring that the SD-WAN device is properly sized to meet network traffic requirements. If the device is overburdened, it can lead to poor performance. Another challenge is ensuring that the quality of service settings are properly configured. If there are conflicts in the traffic prioritization policies, it can lead to poor performance.
Finally, it is important to ensure that the SD-WAN solution’s security features are aligned with business needs and requirements. Some vendors provide built-in security, while others require third-party integrations. Finally, ensuring that the SD-WAN solution provides visibility into applications, users, and devices is also important.
Traditionally, businesses have had to build out costly MPLS circuits or other private networks between each branch office and the data center. This has limited their options for routing traffic and managing connectivity. However, with an SD-WAN, businesses can use the existing public Internet or MPLS connections to improve performance and resiliency across the WAN. This can help them save money while delivering the same or better performance for their business-critical applications. This is possible because an SD-WAN uses multi-transport overlays to route and prioritize applications based on some factors intelligently.
What are the Solutions for SD-WAN?
SD-WAN extends software-defined networking (SDN) to a business network. It automatically routes traffic across network connections based on application needs, quality of service (quality of service) requirements, and circuit costs.
As a result, networks become more cost-efficient and secure. It also improves performance and provides visibility into network traffic patterns. This is especially important because applications are becoming increasingly complex, and the Internet of Things is creating more data that can overtax traditional networks.
The key to addressing these challenges is having a flexible WAN connecting to the cloud and local data centers. SD-WAN does just that, leveraging MPLS and broadband Internet connections to create a smart hybrid WAN that delivers high performance and reduced costs.
Many SD-WAN solutions offer centralized configuration and zero-touch provisioning that reduces the complexity, resources, and opex it takes to deploy new sites. They also support security capabilities like a next-generation firewall, IPS, and a web filter that help to ensure secure connectivity over the public Internet and prevent hackers from intercepting critical information.